Introduction
Cities across the world are investing in sensors and other Internet of Things (IoT) devices in an effort to better understand what is happening in near real-time. Whether that is monitoring if a streetlight is inappropriately off at night or on during the day, whether there is a leak in a water main, or when traffic is backed up on a certain street, cities are interested in providing better services and resolving problems more quickly.
These IoT devices are manufactured by many different companies, transmit data over a number of different communications networks, and store data in thousands of databases on dozens of different cloud services. While cities are able to understand the data being collected by one type of device, that data also tends to be siloed. Cities can find even more insight by centralizing all of the data from multiple devices and legacy systems. This way, if a streetlight is out, they can analyze if that outage had an impact on traffic. If there is an uptick in traffic, they can analyze if traffic lights are working properly or if their timing could be improved.
Centralizing Data with Azure Data Lake
Using the tools offered within the Microsoft Azure Cloud, cities have the opportunity to build a modern data platform that can pull data in from a variety of different sources and allow decision makers to see in near real-time how the information being collected impacts life in the community.
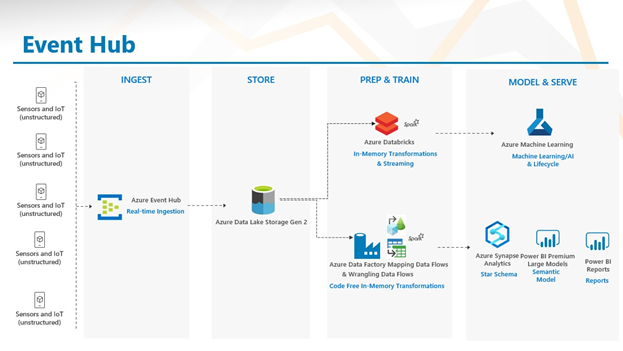
Azure’s Event Hub and IoT Hub enable cities to connect to individual sensors and ingest data in real time. Cities should ensure that the company that makes the sensor allows for programmatic ingestion of data from their sensors. Once the connection is made from Azure Event Hub to the sensor, data can move into an Azure Data Lake. This is where data is centralized and organized for further processing.
Business Intelligence with Azure Synapse and Power BI
Once the data is centralized, cities will want to make sense of the gigabytes of information they suddenly have access to. In one case, cities will want to see the city as it is right now according to the sensor data. Using Azure’s Data Factory and Mapping Data Flows, data can be transformed and loaded into a data warehouse like Azure Synapse. Mapping Data Flows within Azure Data Factory is a low-code tool, accessible to those who may not know how to write in SQL or Python, and is similar to products like SSIS.
Once the data is organized in Azure Synapse, Power BI is able to connect, and then users can build dashboards and reports that allow decision makers to filter and slice data to better analyze the current state.
Predictive Maintenance Using Databricks and Azure Machine Learning Services
In addition to analyzing what is happening currently using tools within Azure, city leaders can predict where issues may arise using the data they are collecting. Using Azure DataBricks, models can be deployed, in near real-time, to identify anomalies (suggesting issues like a water main leak) or to predict where future projects should be taken on to replace entire pieces of infrastructure.
Passing the modeled data from DataBricks to Azure Machine Learning Services also allows cities to operationalize their models and make them accessible to staff beyond the data scientists who wrote the code.
Use Case: Water Authority
3Cloud previously used this approach with a major Water Utility located in the mid-Atlantic. With almost 50,000 sensors deployed in the field, the client wanted to become smarter and more proactive about their water management process. To do this, 3Cloud set out to enable interactive data exploration and reporting without extensive developer investment, while also laying the foundation for advanced analytics capabilities.
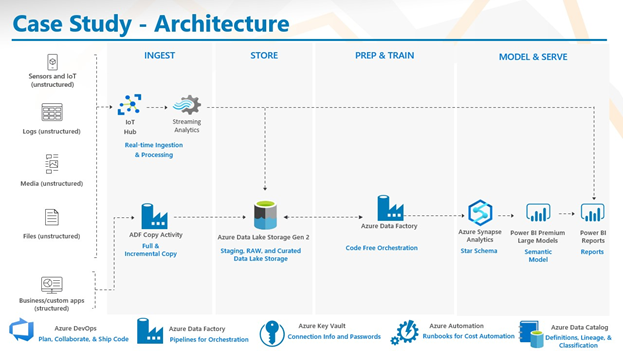
By streaming data from both third-party and directly connected devices, as well as batch ingestion of legacy data from a SCADA system, 3Cloud delivered an architecture with Power BI dashboards that showed both real-time and historic data.
The diagram above details the architecture we built, leveraging IoT Hub and Streaming analytics for real-time ingestion and Azure Data Factory for ingestion of legacy data. Then, the data was all moved into Azure Data Lake. The streaming data was also pushed directly to a Power BI dashboard for real time data viewing, while other data was transformed via Azure Data Factory, loaded into Azure Synapse, and then displayed using Power BI.
Final Considerations
A full modernization of all data infrastructure is rarely available, so planning for how to accommodate these types of applications with modern tools and newer technologies is important.
For cities that are purchasing sensors and managing them directly, the Azure Certified Device Catalog ensures those products will work within the Azure ecosystem. For third party integrations, working with providers to ensure they will allow you to connect to the data they are collecting, so you can ultimately ingest it into a data platform like the one outlined above.
Cities should also consider whether an understanding of the data has to happen the moment it is collected (traffic lights changing based on amount of traffic is a good example here). In this case, data has to be analyzed on the sensor device – or at the edge. The device can collect data, analyze it, and make a decision without the data being sent to the cloud for analysis and then the direction being sent back to the device to react. For use cases that allow for high latency, edge computing is not necessary.
For smart city applications, a number of different categories of staff and end users should be engaged:
- IT and Operations staff to understand the data and technology infrastructure
- Security teams to guard the data and devices
- Field technicians who may need to fix equipment or may get work orders assigned to them by the equipment
- Application developers
- Data scientists to model the data collected
- Top level leadership like Commissioners, Mayors, City Managers and more
- Members of the public where necessary to understand privacy concerns or other ideas for how to use the data and technology
- Educational institutions to engage students in the work being done
3Cloud is able to help your city brainstorm smart city use cases and then implement the underlying data infrastructure to get the most value out of the data being collected. Contact us today!